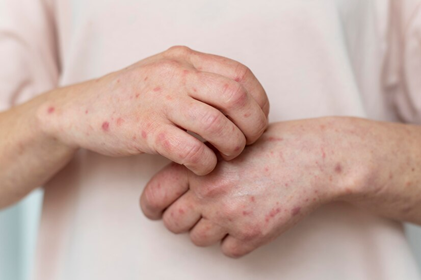
Dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, refers to skin inflammation that results in red, itchy, and often painful patches. It can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-lasting), and various factors contribute to its development.
Causes of Dermatitis
- Allergens: Contact with substances like metals (nickel), latex, cosmetics, or certain plants.
- Irritants: Harsh chemicals, detergents, soaps, and solvents that strip away the skin’s natural oils.
- Genetics: Family history of allergic conditions or sensitive skin.
- Environmental Factors: Cold or dry weather, humidity, or excessive sweating.
- Stress: Emotional stress can exacerbate symptoms.
Types of Dermatitis
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Common in children, often associated with asthma or hay fever.
- Contact Dermatitis:: Reaction to allergens upon contact.Irritant: Caused by direct exposure to irritants.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Affecting oily areas like the scalp, face, and upper chest.
- Nummular Dermatitis: Circular patches of irritated skin, often triggered by dry conditions.
- Stasis Dermatitis: Due to poor circulation, it occurs in the lower legs
Symptoms of Dermatitis
- Itching: Intense itching that worsens with scratching.
- Redness and Inflammation: Skin appears red, swollen, and may develop blisters or crusts.
- Dryness and Scaling: Skin becomes dry, flaky, and may crack or peel.
- Pain and Discomfort: Irritated skin can be painful, especially if infected.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: Assessment of skin appearance and distribution of lesions.
- Skin Patch Testing: Identifying allergens in contact dermatitis cases.
- Skin Biopsy: Occasionally performed to confirm the diagnosis in difficult cases.
Treatment Options
- Topical Treatments:Emollients: Moisturizers to hydrate and protect the skin barrier.Corticosteroids: Anti-inflammatory creams or ointments to reduce itching and redness.Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Alternative to steroids for sensitive areas.
- Oral Medications: To relieve itching, or antibiotics for infected dermatitis.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to UV light to reduce inflammation and itching.
Management and Prevention
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid allergens or irritants that provoke dermatitis.
- Skin Care Routine: Gentle cleansing with mild soap and moisturizing regularly.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation or yoga to reduce stress levels.
- Dermatologist Consultation: Regular check-ups and adjustments to treatment as needed.